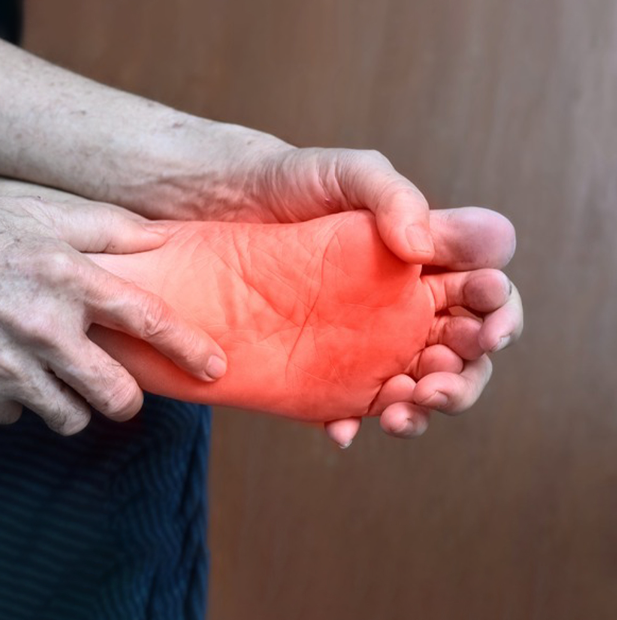
Recognizing warning signs of diabetic foot complications and taking preventive measures are crucial for individuals with diabetes. Here are detailed tips on how to identify warning signs and ways to prevent diabetic foot issues:
Recognizing Warning Signs of Diabetic Foot Complications
Persistent Pain or Numbness:
Look for ongoing pain, tingling, burning, or numbness in your feet or legs. These can be signs of nerve damage (neuropathy).
Changes in Skin Colour and Temperature:
Noticeable changes such as redness, blueness, or unusual warmth or coolness of your feet could indicate circulation problems.
Foot Ulcers or Sores:
Be alert to any open sores, wounds, or ulcers that are slow to heal or show signs of infection. These require immediate medical attention.
Swelling:
Unexplained swelling in your feet or ankles may be a sign of poor circulation or other underlying issues.
Ingrown Toenails or Calluses:
Watch for ingrown toenails or thickened calluses that, if not properly managed, can lead to skin breakdown and infection.
Foot Deformities:
Changes in the shape of your feet, such as hammertoes or bunions, can create pressure points and lead to foot problems.
Decreased Sensation:
Loss of sensation (inability to feel pain, heat, or cold) in your feet is a serious warning sign of nerve damage and requires immediate medical evaluation.
Drainage or Odour:
Any unusual discharge or foul odor from a sore or wound on your foot can indicate infection and should be addressed promptly.
Ways to Prevent Diabetic Foot Complications
Daily Foot Inspection:
Check your feet every day for cuts, blisters, redness, swelling, or any signs of infection. Use a mirror to see the bottoms of your feet or ask someone for help if needed.
Keep Feet Clean and Moisturized:
Wash your feet daily with lukewarm water and mild soap. Dry them thoroughly, especially between the toes, and use a moisturizer to keep the skin soft (avoid applying it between the toes).
Trim Nails Carefully:
Trim your toenails straight across and file the edges to prevent ingrown nails. If you have difficulty doing this, consider seeing a podiatrist.
Wear Proper Footwear:
Choose shoes that fit well and provide ample support and protection. Avoid shoes that are too tight or have seams that could rub against your feet. Always wear socks to prevent friction and blisters.
Avoid Going Barefoot:
Protect your feet from injury by wearing shoes or slippers at all times, even indoors. Check inside your shoes before putting them on to ensure there are no foreign objects.
Manage Blood Sugar Levels:
Keep your blood sugar levels within your target range to prevent nerve and blood vessel damage that can lead to foot complications.
Quit Smoking:
Smoking restricts blood flow to your feet, making it harder for wounds to heal. Quitting smoking can improve circulation and reduce the risk of foot complications.
Regular Exercise:
Engage in regular physical activity to improve circulation and nerve function in your feet. Consult your healthcare provider before starting a new exercise routine.
Routine Healthcare:
Visit your healthcare provider regularly for foot exams. They can detect early signs of foot problems and provide appropriate treatment.
Wear Proper Socks:
Choose moisture-wicking socks that fit well and provide cushioning. Avoid tight socks and those with seams that could cause irritation.
Conclusion
By following these preventive measures and being vigilant about recognizing warning signs, individuals with diabetes can significantly reduce their risk of developing serious foot complications. Regular consultations with healthcare providers, including podiatrists, are essential for maintaining foot health.

Kerala’s leading Ayurvedic healthcare center, offering holistic treatments guided by the best Ayurvedic doctors.
Stay informed and never miss out on the latest news, health tips.
Copyright 2024 © Iravata All Right Reserved.